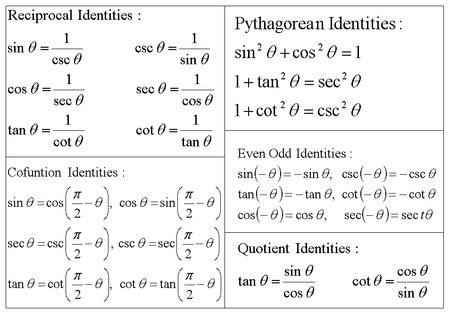
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Reciprocal identities sinu= 1 cscu cosu= 1 secu tanu= 1 cotu cotu= 1 tanu cscu= 1 sinu secu= 1 cosu Pythagorean Identities sin 2ucos u= 1 1tan2 u= sec2 u 1cot2 u= csc2 u Quotient Identities tanu= sinu cosu cotu= cosu sinu CoFunction Identities sin(ˇ 2 u) = cosu cos ˇ 2 u) = sinu tan(ˇ 2 u) = cotu cot(ˇ 2 u) = tanu csc(ˇ 2 u) = secu sec(ˇ 2 u) = cscuDefinition of the Trig Functions Right triangle definition For this definition we assume that 0 2 pThe other four trigonometric functions (tan, cot, sec, csc) can be defined as quotients and reciprocals of sin and cos, except where zero occurs in the denominator It can be proved, for real arguments, that these definitions coincide with elementary geometric definitions if the argument is regarded as an angle given in radians
What Does It Mean To Prove A Trigonometric Identity Socratic
